What Structure Keeps Harmful Chemicals Out Of Animal Cells?

Thecell structure is defined past the cell membrane, the cytoplasm, and the nucleus. A cell is the smallest unit of life and its structure helps it to work every bit the basic building cake of biology.
The prison cell function is to go on all of the functions of the trunk performing equally intended. This includes keeping toxins out of the body, help to break down waste product, brand nutrients and act every bit barriers within organelles.
Cells are the basic building blocks of life. Notwithstanding what are all the components of a prison cell that enable them to carry out their basic functions? Cells are fabricated up of a wide variety of structures and components, and each component plays a necessary and important function.
"The body is a community fabricated upward of its innumerable cells or inhabitants." — Thomas A. Edison
Different types of cells accept dissimilar structures, depending on the function of the prison cell. Sure cells like algae cells, for instance, accept a tail that helps them propel themselves through the water. While other cells like pollen take little spikes on them then they can stick to insects.
Despite their differences, virtually cells have structures in common. These common structures include a prison cell membrane, DNA, ribosomes, and cytoplasm.
Four Central Parts of a Cell: Cell Membrane, Cytoplasm, Deoxyribonucleic acid and Ribosomes
Cells have a plasma membrane, cell membrane, or cell wall that surrounds the prison cell and acts as their skin. Information technology makes upwards the boundary between the prison cell and their environment and controls what can move in and out of the cell. The cell membrane is synthetic out of a phospholipid bilayer, two layers of lipids facing reverse directions. The lipid layers are made out of building blocks of fatty acids and consist of a head and body. The body of the lipid is hydrophobic, pregnant it repels water while the heads of the lipids are hydrophilic, meaning that it likes water.
In addition to the prison cell membrane found in beast cells, plant cells besides have a cell wall. The cell wall is made out of cellulose and it helps give the jail cell extra protection and support. A crucial difference is that unlike prison cell membranes, cell walls exercise not allow for the passage of materials through them. To become around this trouble, cell walls have unique structures chosen plasmodesmata, special holes that allow the material to move in and out.
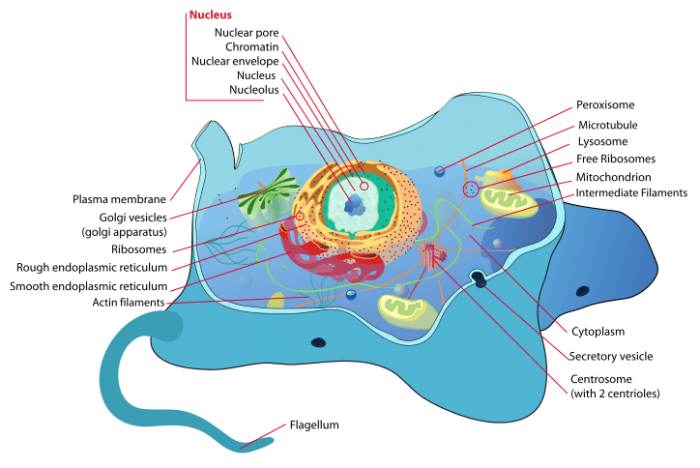
Photo: By LadyofHats (Mariana Ruiz) – Own work using Adobe Illustrator. Image renamed from Prototype: Animal cell construction.svg, Public Domain, https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/alphabetize.php?curid=4266142
The cell membrane holds in a cell'southward cytoplasm. The cytoplasm is a jelly-like substance, made up of mostly h2o, that keeps the various organelles within the prison cell separate from each other. Many of the cell'southward biochemical reactions, like metabolic processes, occur within the cytoplasm.
There are gaps in a cell'southward plasma membrane referred to as pores or channels. These pores or channels are made out of proteins and they control what chemicals, like h2o and nutrient, are able to move into the jail cell.
Deoxyribonucleic Acrid, or Deoxyribonucleic acid, is frequently referred to as "the blueprints for life" and information technology contains the generic information that allows cells to reproduce and perform their respective functions. The Dna of a cell is held within the nucleus of the cells, specifically within the nucleolus.
The cell's nucleus is often referred to as the "brain" of the jail cell, or the control middle. It is the largest part of the cell inside the cytoplasm. Cells that have nuclei are found in plants, animals, algae, protozoa, and fungi. Bacterial cells do not have a nucleus. The nucleus is home to a smaller construction within it called the nucleolus. The nucleolus is an organelle that creates ribosomes. The nucleus has nuclear pores that allow the ribosomes to exit the nucleus and for other materials to move in.
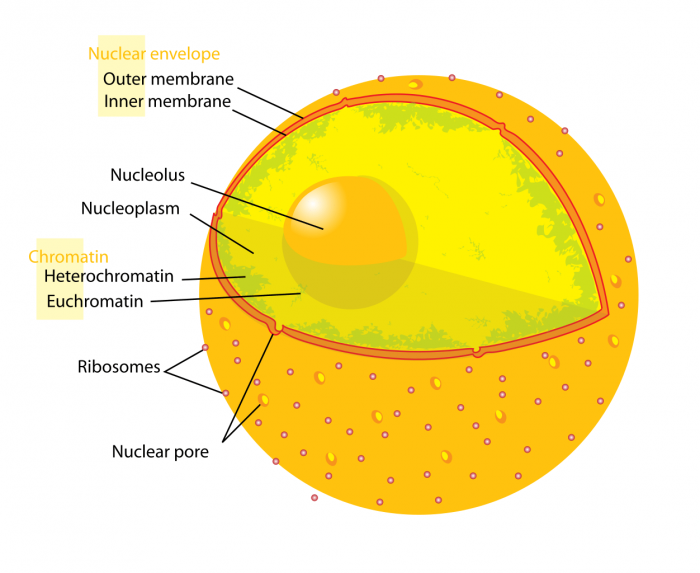
The nucleus has pores that allow the ribosomes to move in and out. Photo: Mariana Ruiz, LadyofHats via Wikimedia Commons, Public Domain
The ribosomes themselves are organelles which assist in the creation of proteins. Proteins are necessary for the prison cell to behave out its essential functions. Ribosomes are made out of one large piece and one smaller unit of measurement. Both of the subunits in the ribosomes assistance in the creation of proteins when they come together with messenger RNA. Though some ribosomes tin exist found in the cytoplasm itself, most of the ribosomes are found in the endoplasmic reticulum. The proteins that ribosomes create while attached to the endoplasmic reticulum will motility from the prison cell to exercise work inside the trunk or volition remain within the cell to synthesize the proteins that the jail cell needs.
Other Important Parts of a Cell
The endoplasmic reticulum (ER) is made out of various membranes, and it synthesizes proteins and for the cell. The endoplasmic reticulum is referred to equally "crude ER" when it has the ribosomes attached to it, and it is chosen "smoothen ER" when at that place are no ribosomes attached to it. The rough endoplasmic reticulum synthesizes the proteins, while the smooth endoplasmic reticulum performs ii functions. The polish ER synthesizes lipids for use in the cell, just information technology besides detoxifies harmful substances.
Afterwards the proteins of the cell take been synthesized past the ribosomes on the endoplasmic reticulum, they are distributed past an organelle called the "Golgi complex". The Golgi complex sorts the proteins out and then sends them to the area that they are needed in. In this respect the Golgi complex is similar a postal service role, distributing packages to their destinations.
The mitochondria are organelles that are responsible for converting the food eaten by an organism into energy. Food is converted into units of energy called ATP by the mitochondria and every jail cell has differing amounts of mitochondria depending on the cell's function and needs. Cells that practice more work, like heart cells, need more mitochondria than other cells.
Plant cells have chloroplasts, while beast cells don't. The chloroplasts in a institute cell are where photosynthesis happens, converting the free energy from the dominicus into chemical energy that the plant cells can utilise. Plant cells also take a vacuole or seemingly big empty space in the middle of the cell. Still, the vacuole of a plant cell actually contains important chemicals similar sugar and water.
Tiny organelles called vesicles can as well be found floating around within the cytoplasm. The vesicles are responsible for conveying materials in, out, and around the cell. The vesicles conduct cloth from 1 role of the cell to another, but they also transport waste material products exterior the prison cell in a process chosen exocytosis.
In that location are likewise some small structures institute in the cytoplasm that bear out various functions depending on the type of cell. Peroxisomes are responsible for collecting toxic chemicals and breaking them downward into harmless byproducts, while centrioles are unique to fauna cells and they guide the division and organisation of chromosomes equally cells split. Finally, lysosomes are structures secreted by the Golgi apparatus which can take large molecules and break them apart into smaller chunks the jail cell tin can utilize.
Cells are circuitous systems with many moving parts that work together to class the various abundance of life we all effectually united states.
Source: https://sciencetrends.com/breakdown-cells-structures-functions/
Posted by: stewartasher1959.blogspot.com

0 Response to "What Structure Keeps Harmful Chemicals Out Of Animal Cells?"
Post a Comment